Calibrating your OLED TV for HDR and Dolby Vision is the key to unlocking the full potential of your panel. Whether you’re watching movies, gaming in 4K120, or fine-tuning your home theater setup, the right calibration steps can dramatically improve brightness handling, shadow detail, color accuracy, and tone mapping performance. This guide walks you through a complete 2026 workflow for SDR, HDR10, and Dolby Vision calibration, from preparation to advanced adjustments—no fluff, just what matters.
Why Calibration Matters
Most OLED TVs ship with presets designed to impress on store shelves—usually “Vivid”, “Dynamic”, or overly bright picture modes. These modes push aggressive processing, oversaturated colors, and unpredictable tone-mapping that break creative accuracy. Calibration fixes this by aligning the display to correct standards: D65 white point, Rec.709 or P3 color gamuts, and proper gamma/EOTF curves for SDR and HDR.
For Dolby Vision, the benefit is even greater. The dynamic metadata can deliver stunning highlight behavior and perfect shadow detail, but only when base settings like white balance, tone-mapping, and panel brightness are dialed in correctly. A poorly configured OLED can crush blacks, clip highlights, or introduce color errors that ruin the cinematic effect.
What You Need
- A modern OLED TV with HDR10 and Dolby Vision support.
- Ability to control room lighting (dim or dark environment).
- Optional: colorimeter, spectroradiometer, and calibration software.
- USB drive with good HDR and Dolby Vision test patterns.
- Streaming device, Blu-ray player, or console capable of outputting HDR.
- High-quality HDMI 2.1 cable.
- Updated firmware and input settings (HDMI “enhanced” mode).

Preparing the TV
Before making adjustments, warm the TV for at least 30 minutes. OLED panels stabilize as they warm up, and early calibration on a cold panel can lead to inaccurate white balance or luminance tracking. After warming up, disable all energy-saving features, Eco mode, Auto Brightness, AI Brightness, and ambient sensors. These will interfere with consistent results.
Enable the HDMI input format you need—“Enhanced” or “4K 120Hz + HDR”. Double-check that the source device (console, PC, streaming stick) outputs HDR or Dolby Vision correctly. Some require manual toggles to activate HDR output.
Calibrating SDR (Baseline)
SDR is the foundation. When SDR is calibrated properly, HDR and Dolby Vision are easier to tune. Start with an accurate picture mode such as “Cinema”, “Filmmaker Mode”, or “Expert (Dark Room)”. These modes disable most processing and expose granular controls like 2-point or 20-point white balance adjustments.
SDR uses BT.709 color space and gamma 2.2–2.4 depending on your room. Dark rooms benefit from 2.4; brighter rooms may use 2.2. Ensure noise reduction, sharpness enhancements, and motion smoothing are off or minimal. Use simple brightness and contrast patterns to verify black level (no crushing) and white level (no clipping).
SDR White Balance
D65 is the target white point (6500K). Many TVs label this setting as “Warm 2” or “Expert Warm”. Even without a meter, choosing the warmest accurate preset is better than “Cool” or “Neutral”, which are far from reference accuracy.
Calibrating HDR10
HDR10 uses static metadata, so it does not adjust dynamically like Dolby Vision. Once HDR triggers (via USB, streaming, or console output), the TV switches to HDR-specific picture modes. OLED Light should be at 100% to allow the panel to reach peak brightness levels needed for HDR highlights. Disable Dynamic Tone Mapping during calibration so EOTF tracking is accurate.
In HDR10, color space expands to P3 within Rec.2020 container. Tone mapping follows the ST 2084 curve. Check highlight clipping with HDR test patterns and verify that shadow details remain visible without raising the black floor.
Calibrating Dolby Vision
Dolby Vision is where OLED TVs truly shine. The dynamic metadata adjusts scene by scene, producing accurate highlight behavior and incredible depth. Triggering Dolby Vision content switches the TV into a DV-specific mode such as “Cinema”, “Cinema Home”, or “Filmmaker Mode”. For calibration accuracy, use “Cinema” or “Filmmaker”; these disable heavy processing.
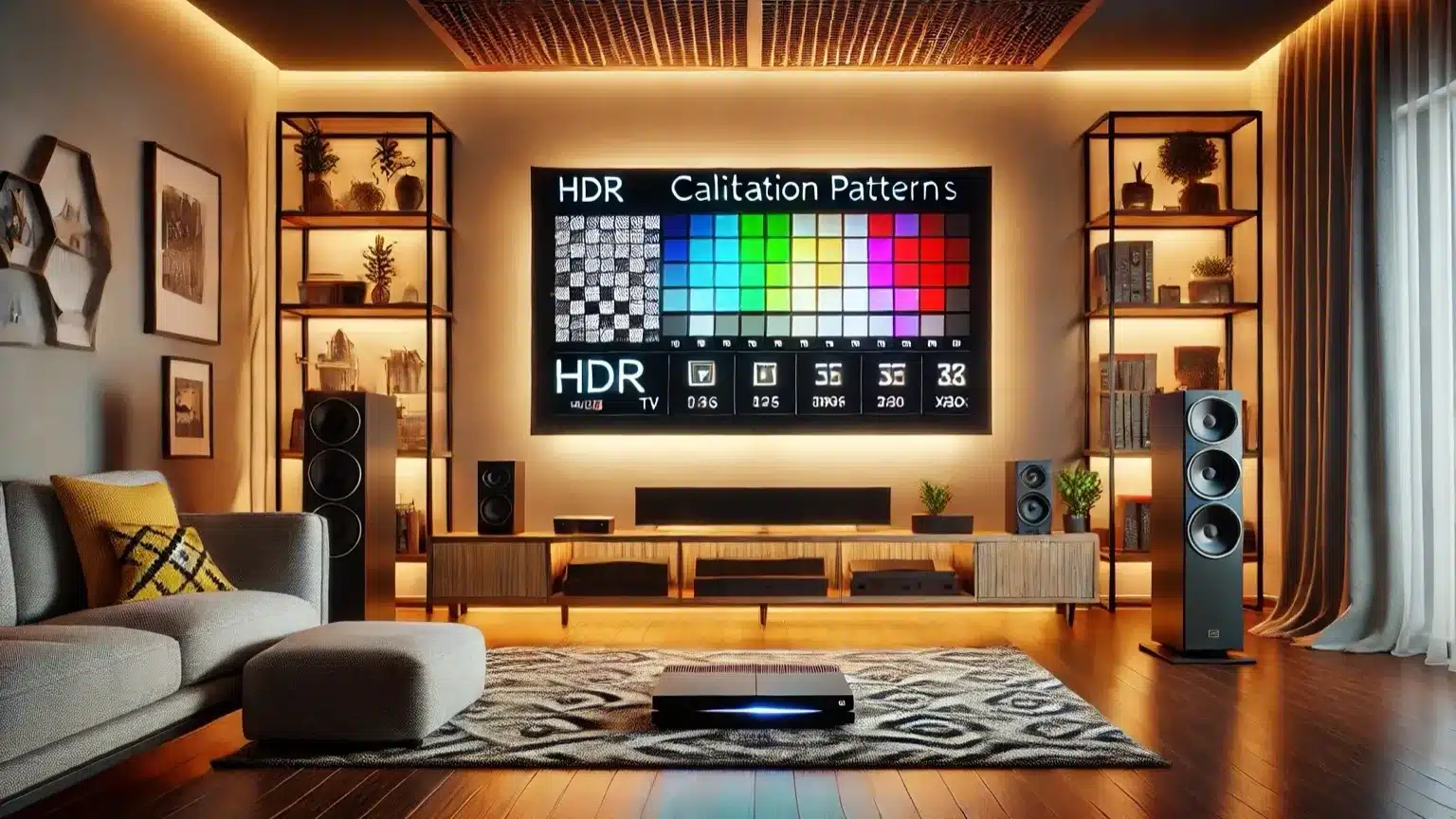

Keep OLED Light at maximum. Disable automatic tone mapping or DV IQ during calibration. Once done, you can re-enable DV IQ if you like ambient-aware adaptation. As with HDR10, white point is D65, and the EOTF follows ST 2084. Check sample DV clips for banding, poor shadow detail, or clipped highlights.
Validating Calibration
Once SDR, HDR10, and Dolby Vision are calibrated, validate by playing real content. Look for natural skin tones, clean gradients, non-blown-out highlights, and consistent shadow detail. If you watch in a very dark room, consider a slightly dimmer brightness setting for comfort—but avoid pushing brightness too low or you risk crushing detail.
Key Settings Checklist
- OLED Light: Max for HDR and DV; moderate for SDR.
- Picture Mode: Use accurate modes like Cinema, Filmmaker, or Expert.
- Color Temperature: Always D65/Warm 2.
- Sharpness: 0–10 depending on brand; avoid oversharpening.
- Noise Reduction: Off.
- Dynamic Tone Mapping: Off for calibration; optional On afterward.
- Gamma/EOTF: 2.2–2.4 (SDR), ST 2084 (HDR/DV).
What You Can and Cannot Fix Without Professional Tools
You Can Fix
- Basic white balance using built-in controls.
- Shadow clipping through brightness controls.
- Highlight clipping by adjusting HDR tone mapping.
- Oversaturated colors by selecting the right mode.
You Cannot Fix
- Panel uniformity issues such as tinting or banding.
- True full-panel 3D LUT color accuracy.
- Factory-level calibration drift without a meter.
- Amazon: AFFILIATE_LINK_1
- AliExpress: AFFILIATE_LINK_2
- Official Store: AFFILIATE_LINK_3
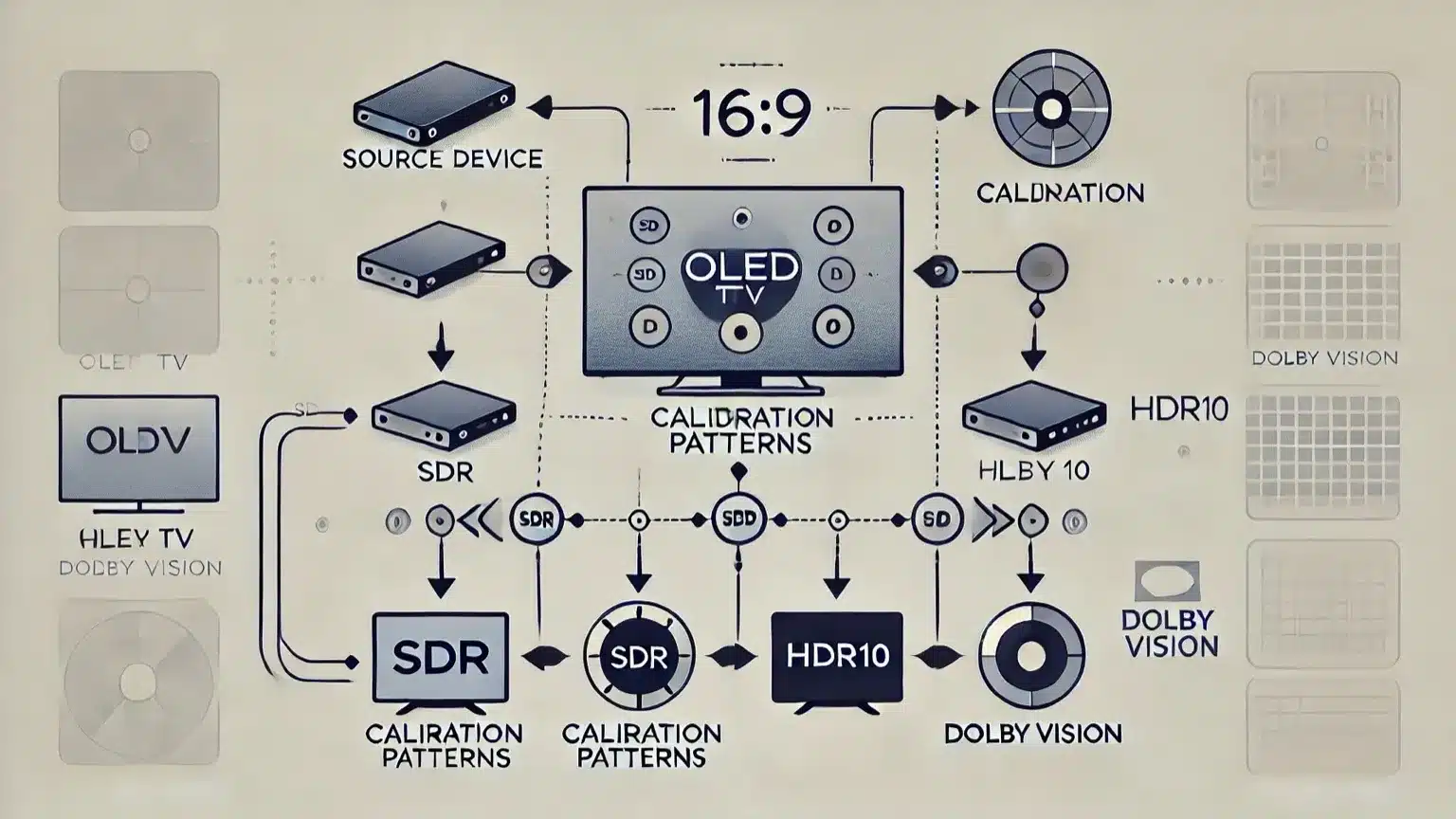
Calibration Workflow Diagram
This diagram illustrates the full workflow of SDR → HDR10 → Dolby Vision calibration, showing how calibration patterns flow from your source device to the OLED panel.
Internal & External Links
For more display recommendations and best practices, check our TV guide:
Best OLED TVs 2026.
For official Dolby Vision display guidelines, refer to:
Dolby Vision HDR Display Standards
.
- Amazon: AFFILIATE_LINK_4
- AliExpress: AFFILIATE_LINK_5
- Official Store: AFFILIATE_LINK_6
FAQ
Do I need a meter for accurate calibration?
No. Most people see massive improvements using correct presets and basic adjustments.
Does calibration make HDR darker?
It may reduce the “fake pop” of Vivid modes, but accuracy increases. You can boost OLED Light if needed.
Should I calibrate each HDMI input?
You only need to calibrate the picture modes you actually use.
Is calibration worth it in bright rooms?
Yes. Just raise OLED Light for daytime viewing.
How often to recalibrate?
Every 12–24 months unless you notice color drift or unusual behavior.










1 thought on “Calibrate Your OLED TV for HDR & Dolby Vision (2026)”